3Risk
Management
(GRI 2-12; 2-13; 2-15, 201-2) (SASB FN-IN-450a.1;
FN-IN-450a.2; FN-MF-450a.3)
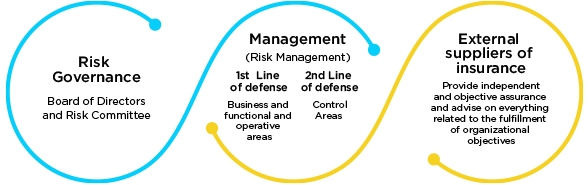
We have a regional Risk Committee and local committees by country.
The Board is responsible for ensuring an adequate environment for risk management, as well as for fostering an internal environment that facilitates its development.
It is responsible for overseeing the implementation of the relevant prevention, control, and response activities, always supported by the Regional Risk Committee, as well as by the local committees of the countries. It is the responsibility of the Senior Management to plan and monitor risks through specialized teams by subsidiary and country.
The Board reviews and updates the risk and performance matrix quarterly, by categories.
For its part, the Chairman of the Risk Committee, together with the subsidiary’s team, are responsible for analyzing and providing the necessary measures that mitigate a latent or present risk.
Model 3 Defense Lines
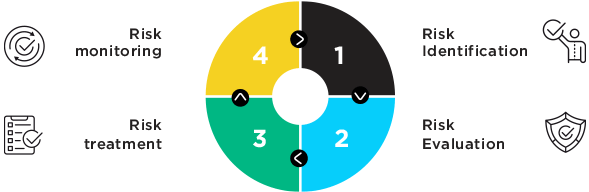
Risk Identification and Management Process in FFG
Operation Risk management methodoly
3.1 Main Risks Identified by FFG:
3.2 Climate Change Risks
For second consecutive year,we have conduced a climate change risk identi cation exercise under the nomenclature of Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). As a nancial institution, we are exposed to climate risks and opportunities directly, through our operations and the use of natural resources and indirectly, through nancial intermediation activities with borrowers, clients, and counterparts.
Transition risks: The transition to a low-carbon economy can entail major political, legal technological and market changes to address mitigation and adaptation requirements related to climate change. Depending on the nature, speed and approach of these changes, transition risks can pose financial and reputational risks at di erent levels for the organizations.
Physical risks: Physical risks from climate change can lead to (acute)events or long-term (chronic) changes in climate patterns. They may have financial implications for organizations such as direct damage to assets or indirect impacts from production chain disruptions.
Transition risks identified in FFG:
Acute
Risks
Risks
Risks
